
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Jinan University, College of Physics and Optical Engineering, Guangdong Provincial Engineering Technology Research Center of Vacuum Coating Technologies and New Energy Materials, Guangzhou Key Laboratory of Vacuum Coating Technologies and New Energy Materials, Guangzhou, China
2 Jinan University, College of Physics and Optical Engineering, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Guangzhou, China
3 Zhengzhou University, School of Physics and Microelectronics, Key Laboratory of Materials Physics of Ministry of Education, Zhengzhou, China
4 Jinan University, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Guangzhou, China
5 Jianghan University, School of Optoelectronic Materials and Technology, Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Chemical Materials and Devices of Ministry of Education, Wuhan, China
Despite the rapid advances of red and green perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs), achieving high brightness with high external quantum efficiency (EQE) remains a challenge for the pure-blue PeLEDs, which greatly hinders their practical applications, such as white-light illumination and in optical communication as a high-speed and low-loss light source. Herein, we report a high-performance pure-blue PeLED based on mixed-halide quasi-2D perovskites incorporated with a zwitterionic molecule of 3-(benzyldimethylammonio) propanesulfonate (3-BAS). Experimental and density functional theory analysis reveals that 3-BAS can simultaneously eliminate non-radiative recombination loss, suppress halide migration, and regulate phase distribution for smoothing energy transfer in the mixed-halide quasi-2D perovskites, leading to the final perovskites with high photoluminescence quantum yield and robust spectrum stability. Thus, the high-performance pure-blue PeLED with a recorded brightness with 1806 cd m - 2 and a relative higher EQE of 9.25% is achieved, which is successfully demonstrated in a visible light communication system for voice signal transmission. We pave the way for achieving highly efficient pure-blue PeLEDs with great application potential in future optical communication networks.
pure-blue PeLEDs quasi-2D perovskite zwitterionic additive visible light communication Advanced Photonics
2024, 6(2): 026002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Engineering Research Center on Visible Light Communication of Guangdong Province, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Key Laboratory of Visible Light Communications of Guangzhou, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
Side polished fiber (SPF) has a controllable average roughness and length of the side-polishing region, which becomes a versatile platform for integrating multiple materials to interact with the evanescent field to fabricate all-fiber devices and sensors. It has been widely used in couplers, filters, polarizers, optical attenuators, photodetectors, modulators, and sensors for temperature, humidity, strain, biological molecules, chemical gas, and vector magnetic monitoring. In this article, an overview of the development history, fabrication techniques, fiber types, transmission characteristics, and varied recent applications of SPFs are reviewed. Firstly, the fabrication techniques of SPFs are reviewed, including the V-groove assisted polishing technique and wheel polishing technique. Then, the different types of SPFs and their characteristics are discussed. Finally, various applications of SPFs are discussed and concluded theoretically and experimentally, including their principles and structures. When designing the device, the residual thickness and polishing lengths of the SPF need to be appropriately selected in order to obtain the best performance. Developing all-fiber devices and sensors is aimed at practical usability under harsh environments and allows to avoid the high coupling loss between optical fibers and on-chip integrated devices.
Side polished fiber (SPF) V-groove assisted polishing technique wheel polishing technique lab-on-fiber fiber devices sensors Photonic Sensors
2023, 13(1): 230120
1 暨南大学 1. 理工学院 光电工程系
2 2. 光电信息与传感技术广东普通高校重点实验室
3 暨南大学 2. 光电信息与传感技术广东普通高校重点实验室
4 3. 广东省光纤传感与通信技术重点实验室, 广州 510632
磁流体具有优异的磁光特性, 为光纤磁场传感器的实现提供了一种新途径, 经过十多年发展, 已经成为光纤磁传感领域的一个重要研究方向。目前, 已有大量的基于不同结构和原理的磁流体型光纤磁场传感器被相继提出, 且总体上经历了从标量到矢量磁场传感的发展, 文章以该发展脉络为主线, 对磁流体的磁光特性、传感器的实现方法进行梳理和总结, 最后指出当前仍存在的一些问题并进行展望。
光纤传感 磁场测量 磁流体 optical fiber sensing magnetic field measurement magnetic fluids
1 中山火炬职业技术学院 光电信息学院,广东 中山 528436
2 工业和信息化部 电子第五研究所,广州 510610
3 暨南大学 广东省可见光通信工程技术研究中心,广州 510632
4 暨南大学 广州市可见光通信工程技术重点实验室,广州 510632
5 湖南航天远望科技有限公司,长沙 410205
基于白光发光二极管(LED)的可见光通信、照明两用系统近年来得到广泛的研究,然而普通LED性能制约了可见光通信调制带宽。为进一步提高LED的调制带宽,可采用微尺寸LED。简要阐述了提高LED调制带宽的方法,综述了近年来在优化可见光通信调制带宽的微尺寸LED性能方面的进展,指出了未来微尺寸LED的研究方向。
可见光通信 微尺寸发光二极管 调制带宽 visible light communication micro-size light emitting diode modulation bandwidth
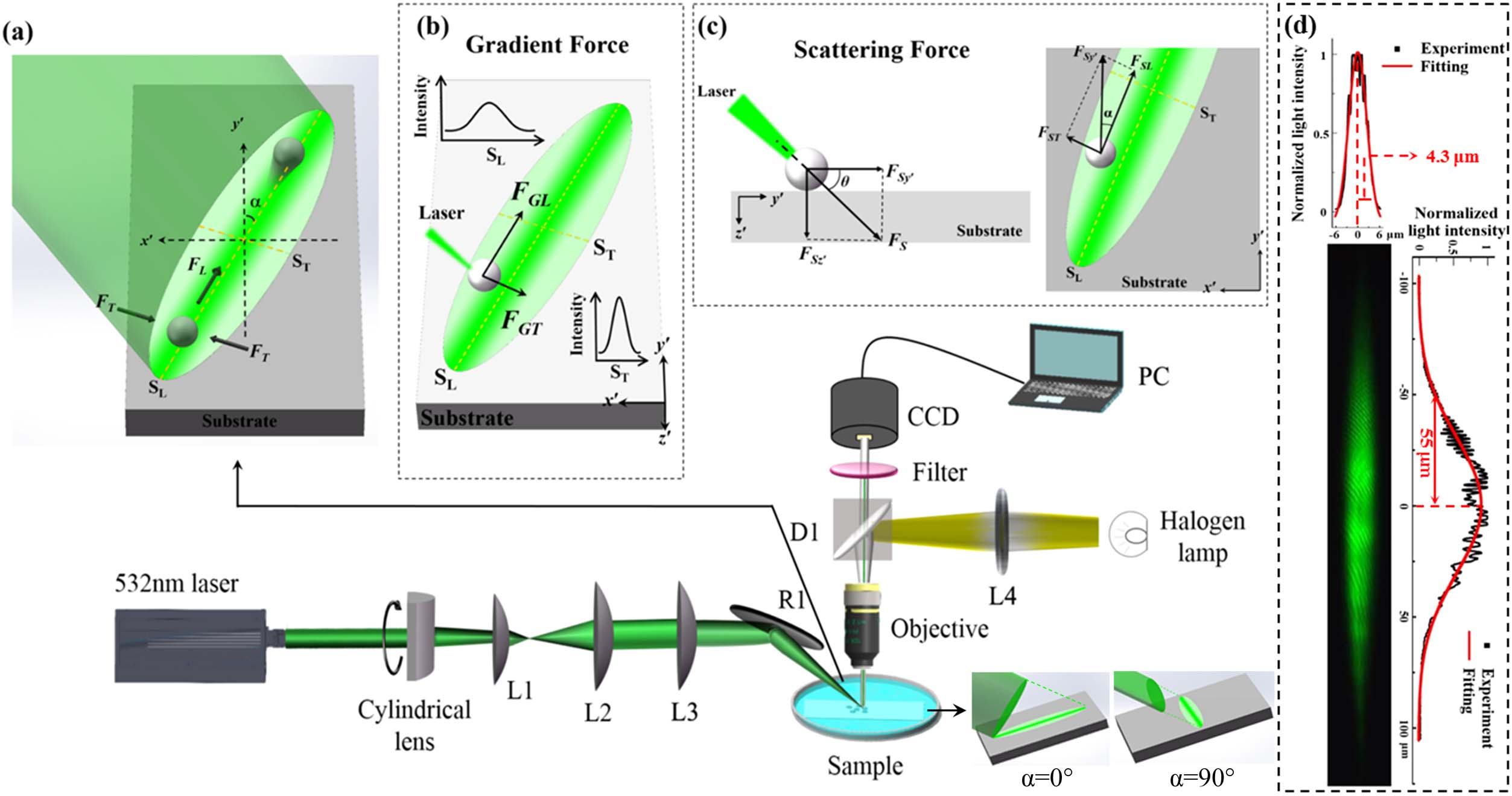
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Department of Cell Biology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut 06510, USA
4 e-mail: thzhechen@jnu.edu.cn
Opto-conveyors have attracted widespread interest in various fields because of their non-invasive and non-contact delivery of micro/nanoparticles. However, the flexible control of the delivery distance and the dynamic steering of the delivery direction, although very desirable in all-optical manipulation, have not yet been achieved by opto-conveyors. Here, using a simple and cost-effective scheme of an elliptically focused laser beam obliquely irradiated on a substrate, a direction-steerable and distance-controllable opto-conveyor for the targeting delivery of microparticles is implemented. Theoretically, in the proposed scheme of the opto-conveyor, the transverse and longitudinal resultant forces of the optical gradient force and the optical scattering force result in the transverse confinement and the longitudinal transportation of microparticles, respectively. In this study, it is experimentally shown that the proposed opto-conveyor is capable of realizing the targeting delivery for microparticles. Additionally, the delivery distance of microparticles can be flexibly and precisely controlled by simply adjusting the irradiation time. By simply rotating the cylindrical lens, the proposed opto-conveyor is capable of steering the delivery direction flexibly within a large range of azimuthal angles, from to 75°. This study also successfully demonstrated the real-time dynamic steering of the delivery direction from to 45° with the dynamical rotation of the cylindrical lens. Owing to its simplicity, flexibility, and controllability, the proposed method is capable of creating new opportunities in bioassays as well as in drug delivery.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(7): 07001124

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Key Laboratory of Visible Light Communications of Guangzhou, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
4 Photonics Technology Laboratory, Centre of Advanced Electronic and Communication Engineering, Faculty of Engineering and Built Environment, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, 43600 UKM Bangi, Selangor, Malaysia
5 e-mail: chenyaofei@jnu.edu.cn
6 e-mail: yunhanluo@163.com
Herein we propose a novel strategy to enhance surface plasmon resonance (SPR) by introducing a photonic cavity into a total-internal-reflection architecture. The photonic cavity, which is comprised of a highly reflective photonic crystal (PC), defect layers, and a gold (Au) film, enables Fabry–Perot (FP) resonances in the defect layers and therefore narrows the SPR resonance width in the metallic surface as well as increases the electric field intensity and penetration depth in the evanescent region. The fabricated sensor exhibits a 5.7-fold increase in the figure of merit and a higher linear coefficient as compared with the conventional Au-SPR sensor. The demonstrated PC/FP cavity/metal structure presents a new design philosophy for SPR performance enhancement.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(4): 04000448

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Department of Optoelectronic Engineering, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 e-mail: qiuwentao@jnu.edu.cn
4 e-mail: ttguanheyuan@jnu.edu.cn
An all-optical light–control–light functionality with the structure of a microfiber knot resonator (MKR) coated with tin disulfide () nanosheets is experimentally demonstrated. The evanescent light in the MKR [with a resonance of and an extinction ratio (ER) of ] is exploited to enhance light–matter interaction by coating a two-dimensional material nanosheet onto it. Thanks to the enhanced light–matter interaction and the strong absorption property of , the transmitted optical power can be tuned quasi-linearly with an external violet pump light power, where a transmitted optical power variation rate with respect to the violet light power of is obtained. In addition, the MKR structure possessing multiple resonances enables a direct experimental demonstration of the relationship between resonance properties (such as and ER), and the obtained variation rate with respect to the violet light power. It verifies experimentally that a higher resonance and a larger ER can lead to a higher variation rate. In terms of the operating speed, this device runs as fast as . This kind of all-optical light–control–light functional structure may find applications in future all-optical circuitry, handheld fiber sensors, etc.
Photonics Research
2018, 6(12): 12001137
1 暨南大学 广州可见光通信工程技术研究中心,广东 广州510632
2 暨南大学 广东高校光电信息与传感技术重点实验室,广东 广州510632
3 暨南大学 广州可见光通信重点实验室, 广东 广州510632
4 暨南大学 理工学院 光电工程系, 广东 广州510632
在复杂光照条件下二维码扫码器采集到的图像容易出现整体高亮、阴影区域和局部高亮、阴影区域, 使得图像分割阈值确定困难, 研究了Sauvola算法中的窗口大小w值和修正因子k值对于QR码图像二值化的影响。针对全局二值化方法抗噪能力差和局部二值化方法处理速度慢的缺陷, 提出了一种改进的QR码图像二值化方法, 将Otsu和Sauvola算法相结合提升算法抗噪能力, 并利用积分图算法提高算法运行效率。实验证明, 该方法二值化效果优于经典的二值化方法, 平均运行效率比原Sauvola算法提高17倍, 提升了识别成功率。
QR码 二值化 修正因子 积分图像 QR code binarization correction factor integral image

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Optical Fiber Sensing and Communications, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
2 Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Information and Sensing Technologies of Guangdong Higher Education Institutes, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
3 Key Laboratory of Visible Light Communications of Guangzhou, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, China
4 School of Physics and Optoelectronic Engineering, Guangdong University of Technology, Guangzhou 510006, China
5 State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies and School of Electronics and Information Technology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
Tungsten disulfide (WS2), as a representative layered transition metal dichalcogenide (TMDC) material, possesses important potential for applications in highly sensitive sensors. Here, a sensitivity-enhanced surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensor with a metal film modified by an overlayer of WS2 nanosheets is proposed and demonstrated. The SPR sensitivity is related to the thickness of the WS2 overlayer, which can be tailored by coating a WS2 ethanol suspension with different concentrations or by the number of times of repeated post-coating. Benefitting from its large surface area, high refractive index, and unique optoelectronic properties, the WS2 nanosheet overlayer coated on the gold film significantly improves the sensing sensitivity. The highest sensitivity (up to 2459.3 nm/RIU) in the experiment is achieved by coating the WS2 suspension once. Compared to the case without a WS2 overlayer, this result shows a sensitivity enhancement of 26.6%. The influence of the WS2 nanosheet overlayer on the sensing performance improvement is analyzed and discussed. Moreover, the proposed WS2 SPR sensor has a linear correlation coefficient of 99.76% in refractive index range of 1.333 to 1.360. Besides sensitivity enhancement, the WS2 nanosheet overlayer is able to show additional advantages, such as protection of metal film from oxidation, tunability of the resonance wavelength region, biocompatibility, capability of vapor, and gas sensing.
Plasmonics Surface waves Optical sensing and sensors Photonics Research
2018, 6(6): 06000485
1 暨南大学光电信息与传感技术广东高校重点实验室, 广东 广州 510632
2 暨南大学光电工程系, 广东 广州 510632
3 广东职业技术学院轻化工程系, 广东 佛山 528041
4 暨南大学化学系, 广东 广州 510632
将还原氧化石墨烯(rGO)沉积在侧边抛磨光纤(SPF)上制作了一种新型的光纤湿度传感器。在高湿度区域[相对温度(RH)为70%~95%],传感器的光功率变化达到6.9 dB,尤其在RH 为75%~95%区域,传感器对湿度变化能实现相关系数为98.2%的线性响应,灵敏度可达0.31 dB/(%RH),响应速度快于0.13 (%RH)/s,并且具有很好的可重复性。对传感机理的理论分析可以解释实验结果,并且表明这种基于石墨烯的光纤传感器亦可广泛应用于其他种类化学气体的探测。这种全新机理的光学传感器是对石墨烯电化学传感器的一种很好的补充,并将促进石墨烯在化学传感技术中的应用。
光纤光学 光纤湿度传感器 还原氧化石墨烯 侧边抛磨光纤 化学气体传感器





